Network Setup:
Install Network Card: Initially you have to insert the network card into the computer by: shut down the computer, remove the computer cover, then you find the empty slot to plug in the network card. Screw the screws. Then close the cover.
Install the driver for the network card: After you have inserted the network card into the computer, when booting up the computer, it will recognize a new device and ask you to provide drivers, then you just put the driver disk into and only the path where Driver storage (you can follow the installation guide included when you buy network card). After the installation is complete you can proceed to set up the network cable connection.
Network cable connection: In this model you use twisted pair to connect. The first requirement is that you have to measure the distance from the node (from the computer) to connect to the network to the hub (possibly Hub or Switch). Then you cut a new twisted-pair cable, and then the two ends of the cable with standard RJ_45. When you're done, just plug one end of the network cable into the network card, and the other end into a central hub port (hub or switch). After connecting the network cable, if you see the light on the port (hub or switch), the light is on, ie the physical link between the hub and the switch is good. Otherwise, you should check that your network cable is properly connected, or that the network card has been installed correctly. After setting up the network, in other words setting up a hardware link between the hub and the node, the nodes can not communicate with each other. Between nodes can communicate with each other, then you have to set the nodes (computers) in the LAN according to a certain standard. A standard is a protocol for exchanging information between two computer systems, or two computer devices. The protocol is also known as the etiquette or convention of a computer network. In a peer-to-peer environment, computers running Microsoft's operating system typically use the TCP / IP protocol (Transmission Control Protocol / Internet Protocol).
TCP / IP settings: To install TCP / IP for each machine: For Win 9x, you proceed:
My computer - & gt; Control Panel - & gt; Network - & gt; If you have seen the TCP / IP then you do not need to add more if you do not have click on the button
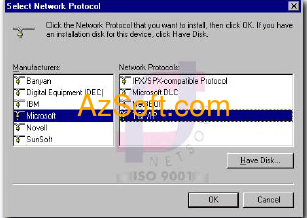
ADD - & gt; to the door
Add Component - & gt; Then you select the same picture
- & gt; select OK
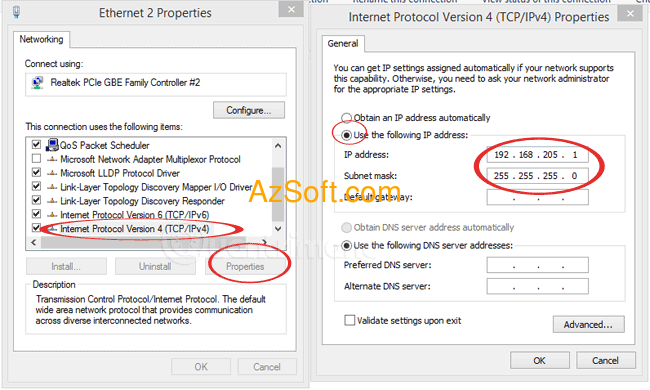
Assign IP to network: When configuring and assigning IPs to a network, there are two main types: Dynamic IP assignment: Normally, after you have successfully physically connected, and assign TCP / IP to each node (computer), the The machine is able to communicate with each other, you do not need to concern IP assignment anymore. Static IP assignment: If you need to set up a network to share resources on the network such as printers, file shares, offline mail settings, or you will install the internet share on any computer. , then configure the other machines to connect to the internet, then you should set IP assignment in static form. Windows 7 or higher, you right-click on the network icon in the system tray
& gt; Open Network and Sharing Center & gt; Change adapter Settings & gt; Right-click on the network name, select
Properties & gt; pull down select
TCP / IPv4 & gt; Properties. Then select and fill as follows:
To make you into
My computer - & gt; Control Panel - & gt; Network - & gt; If you have seen the TCP / IP protocol then you do not need to add it, if not, add it (see instructions above) - & gt; Select TCP / IP and then select Properties. - & gt; You assign the IP as shown and then select OK.
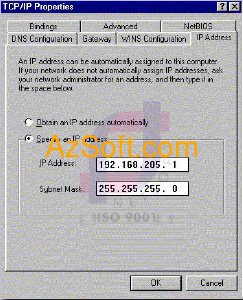
Note: Static TCP / IP addressing is required in peer-to-peer networks using TCP / IP. But with a local network running Windows NT based Client / Server model, you should also set static address to easily manage and detect errors. The computers in the network must have the same IP address and must have the same Subnet Mask (see Figure 02). Once you have completed the above steps, the nodes, the computers in your LAN are able to exchange information to each other, sharing resources between machines.














